This repository contains the necessary files to provide a starting point for a model deployment app which standardizes ML models.
Model deployment is the process of taking a trained machine learning model and making it available for use in a real-world application. This involves a variety of steps, including selecting an appropriate deployment environment, preparing the model for deployment, and creating an interface for users to interact with the model. Deploying a model is an important step in the machine learning pipeline, as it is what enables the model to be used to solve real-world problems. Effective deployment requires careful consideration of factors such as scalability, reliability, and security, and can involve the use of specialized tools and platforms to streamline the process.
Using Inheritance to Standardize HuggingFace Models
Using inheritance in Python is a powerful tool for creating reusable code and standardizing behavior across multiple classes. In the context of deploying Hugging Face models in an application, we can use inheritance to create a ModelWrapper class that standardizes the process of preparing input data and calling the predict method of the Hugging Face model.
The example code for standardizing the models can be found here
The ModelWrapper class can take in the specific differences of each Hugging Face model, such as the tokenizer and model architecture, and use them to modify input data in a standardized way. For example, if one Hugging Face model requires the input to be tokenized and encoded before being passed to the model, the ModelWrapper can use the specified tokenizer to perform these actions. Similarly, if another model requires the input to be preprocessed in a specific way, the ModelWrapper can implement the necessary preprocessing steps.
By standardizing the input modification process, the ModelWrapper allows for easy integration of new Hugging Face models into the deployment app. Additionally, by implementing a predict method that calls the predict method of the Hugging Face model, the ModelWrapper hides the specifics of each model’s prediction process and allows for a consistent interface to be used in the app.
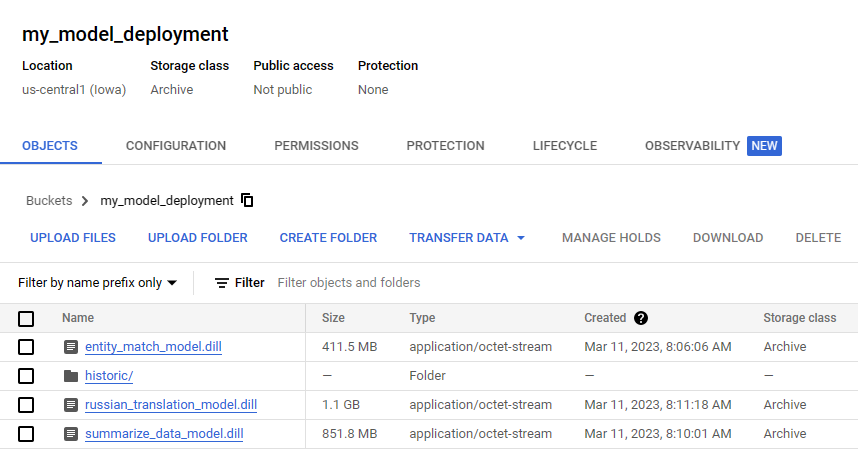
The Model Deployment proposes serialization using the Dill library, after which the serialized files are uploaded to a GCP bucket.
Usage
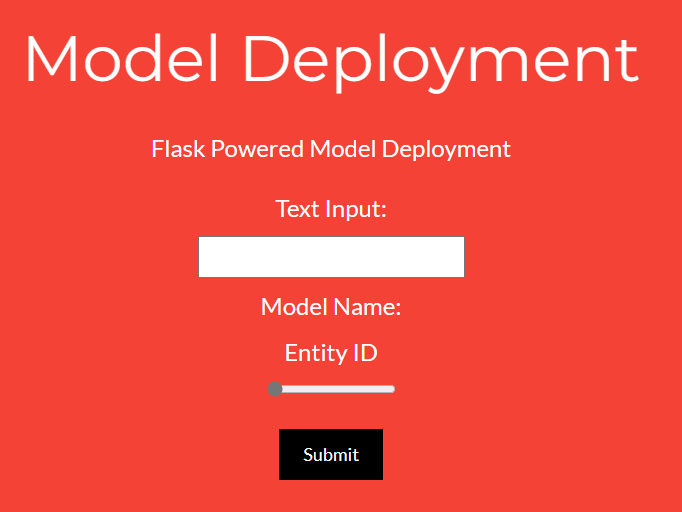
The Model Deployment app creates a Flask server to evaluate the models as well as provide a single endpoint which can make use of the models loaded.
Local
Install the requirements using:
pip install -r requirements.txt
The Flask server can be accessed by running:
python app.py
and navigating to http://localhost:8080 or http://127.0.0.1:8080
Docker
- Clone this repository.
- Build the container using the following command: docker build -t language_models ..
- Run the container using the following command: docker run -it -p 8080:8080 language_models.
- Navigate to http://localhost:8080 in your web browser.
Endpoint
/
A demo of the Model Deployment app can be found here
/predict
The server makes use of a GET /predict endpoint with a JSON payload to consolidate all the requests.
The input format is as follows:
{
"model_name": MODEL_NAME,
"data": TEXT_DATA
}
Where MODEL_NAME is any of the loaded models whcih can be found here and TEXT_DATA is the text input for the models. Returns
{"405": "Method Not Allowed"}
if the request doesn’t have a payload or the Method is Not Allowed.